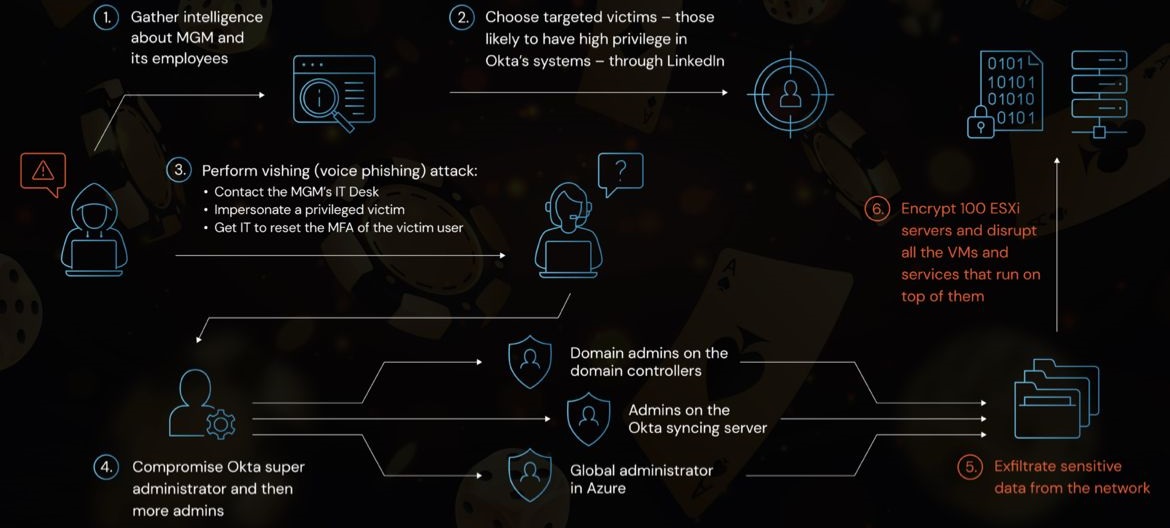
In today's interconnected world, protecting sensitive information has become paramount. The terms "cybersecurity" and "information security" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and scopes. In this article, we will delve into the comprehensive differences between these two concepts, providing a clear understanding of their roles in safeguarding digital assets.
Defining Cybersecurity:
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and digital infrastructure from unauthorized access, damage, or disruption. It encompasses a broad range of measures aimed at defending against cyber threats, such as malware, hacking attempts, and data breaches. Cybersecurity professionals develop and implement strategies to mitigate risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
Scope of Cybersecurity:
Cybersecurity deals specifically with securing digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. It involves measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and vulnerability management. Cybersecurity professionals focus on identifying vulnerabilities, implementing security controls, and monitoring systems for potential breaches. Their primary goal is to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyber-attacks.
Defining Information Security:
Information security, on the other hand, is a broader discipline that encompasses the protection of all forms of sensitive information, regardless of the medium or format in which it is stored or transmitted. It involves a comprehensive approach to safeguarding data, including physical, technical, and administrative controls. Information security aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information throughout its lifecycle, from creation to destruction.
Scope of Information Security:
Information security encompasses a broader perspective, covering all aspects of protecting sensitive information, regardless of the medium. This includes physical documents, intellectual property, employee records, customer data, and more. Information security professionals establish policies, procedures, and controls to ensure data confidentiality, prevent unauthorized disclosure, and maintain data integrity. They address risks associated with both digital and physical assets, including access controls, data classification, and employee awareness training.
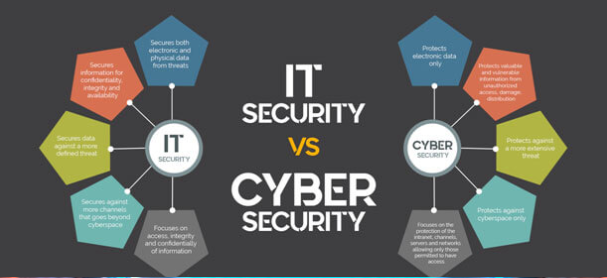
Overlap and Interdependence:
While cyber and information security have distinct scopes, they are interconnected and rely on each other to create a comprehensive security framework. Cybersecurity measures are essential to protect digital assets, including networks and systems, from external threats. Information security, on the other hand, focuses on protecting the data itself, regardless of the means by which it is accessed or stored. A robust information security program enhances cybersecurity efforts by ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
Key Differences:
The primary distinction between cybersecurity and information security lies in their focus. Cybersecurity deals with protecting the digital infrastructure and assets from cyber threats, whereas information security encompasses a broader range of sensitive data protection measures, including physical and administrative controls.
Another key difference lies in the scope of their impact. Cybersecurity primarily concerns external threats that target digital systems and networks. Information security, on the other hand, covers both external and internal threats, acknowledging that data breaches and unauthorized access can occur from within an organization.
Career Paths:
Professionals working in the field of cybersecurity typically focus on technical aspects, such as network security, penetration testing, and incident response. They possess specialized skills in areas like ethical hacking, forensics, and security analysis.
Information security professionals, on the other hand, often have a broader role that extends beyond technology. They work on creating and implementing policies, conducting risk assessments, managing compliance, and educating employees about security best practices.
Conclusion:
While cybersecurity and information security are related disciplines, they have distinct scopes and focuses. Cybersecurity revolves around protecting digital systems and networks from cyber threats, while information security encompasses a broader approach to safeguarding all forms of sensitive information.
Both fields are critical in today's digital landscape, and organizations must ensure a comprehensive security framework that encompasses both aspects. By understanding these differences, organizations can enhance their security posture and protect their digital assets effectively.