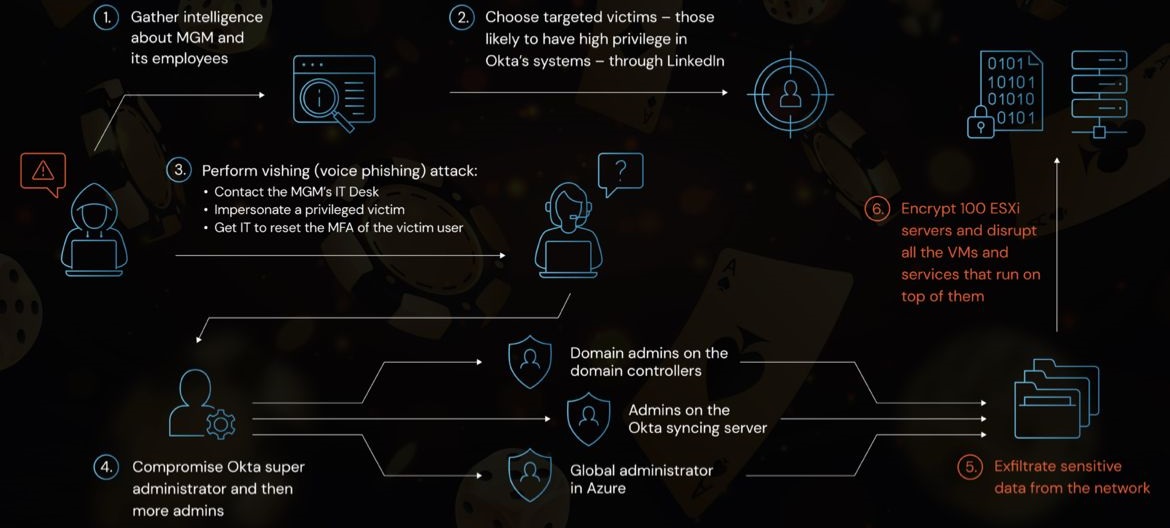
A Chinese cyber espionage group has been found exploiting a VMware ESXi zero-day vulnerability to backdoor guest virtual machines, a new report from cybersecurity firm Mandiant reveals.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-22049, allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a vulnerable ESXi host. This could allow the attacker to gain control of the host and its guest virtual machines, or to install malware on the host.
Mandiant said that the Chinese group, which it calls APT41, has been exploiting the vulnerability since at least December 2022. The group has targeted a variety of organizations, including government agencies, defense contractors, and financial institutions.
VMware released a patch for CVE-2023-22049 on June 14, 2023. Mandiant recommends that organizations install the patch as soon as possible.
How the Attack Works
The CVE-2023-22049 vulnerability exists in the way that ESXi handles certain network packets. An attacker can exploit the vulnerability by sending a specially crafted network packet to a vulnerable ESXi host.
The exploit code will then execute on the ESXi host, giving the attacker control of the host. The attacker can then use the host to gain access to guest virtual machines, or to install malware on the host.
The vulnerability is caused by a flaw in the way that ESXi handles the TCP/IP protocol. When ESXi receives a network packet, it parses the packet and extracts the data from the packet. However, if the packet is specially crafted, ESXi can be tricked into executing arbitrary code.
The exploit code that is used to exploit the vulnerability is a shellcode. A shellcode is a piece of code that is designed to run on a computer system. The shellcode that is used to exploit CVE-2023-22049 gives the attacker control of the ESXi host.
Once the attacker has control of the ESXi host, they can then use the host to gain access to guest virtual machines, or to install malware on the host. The attacker can also use the host to launch other attacks, such as ransomware attacks.
Who is APT41?
APT41 is a Chinese cyber espionage group that has been active since at least 2016. The group has been linked to a variety of attacks, including the theft of intellectual property from defense contractors and the hacking of government agencies.
APT41 is known for its use of sophisticated techniques, including zero-day vulnerabilities and social engineering. The group has also been known to use its access to victim networks to launch other attacks, such as ransomware attacks.
What to Do If You Are Affected
If you believe that your organization has been affected by the CVE-2023-22049 vulnerability, you should take the following steps:
Install the patch for CVE-2023-22049 as soon as possible: VMware has released a patch for the vulnerability, which can be found here: https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2023-0002.html
Review your security logs for any suspicious activity: Look for any unusual activity in your security logs, such as new connections from unknown IP addresses or unusual file changes.
Implement additional security measures to protect your organization from future attacks: These measures could include using a firewall to block malicious traffic, using intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor for suspicious activity, and implementing security awareness training for employees.
If you are concerned that your organization has been compromised, you should contact a security professional for assistance.
Here are some additional tips for protecting your organization from the CVE-2023-22049 vulnerability and other cyber threats:
Keep your software up to date with the latest security patches.
Use a firewall to block malicious traffic.
Implement intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor for suspicious activity.
Implement security awareness training for employees.
Back up your data regularly.
By following these tips, you can help to protect your organization from cyber attacks.
Conclusion
The CVE-2023-22049 vulnerability is a serious threat to organizations that use VMware ESXi. Organizations should install the patch for the vulnerability as soon as possible and review their security logs for any suspicious activity.
In addition to installing the patch, organizations should also implement additional security measures to protect themselves from future attacks. These measures could include using a firewall to block malicious traffic, using intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor for suspicious activity, and implementing security awareness training for employees.
By taking these steps, organizations can help to protect themselves from the CVE-2023-22049 vulnerability and other cyber threats.